What makes MemRussian different?
MemRussian teaches you how to form noun cases, verb conjugations, while simultaneously expanding your vocabulary. This integrated approach ensures that you not only learn new words but also understand their grammatical roles and how they fit into sentences.
What are noun cases?
Overview
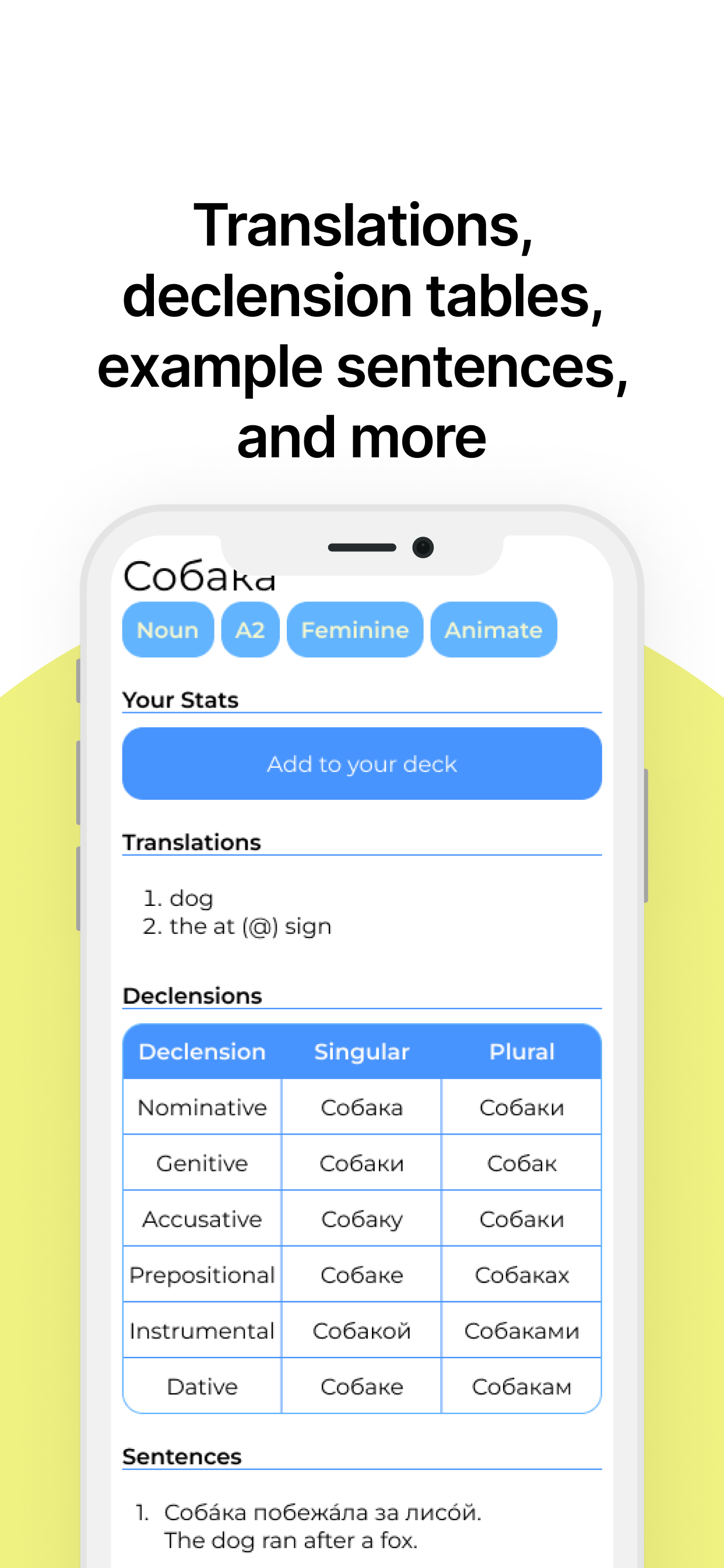
Noun cases are grammatical categories that indicate the role a noun plays in a sentence. In Russian, there are six primary cases, each serving a specific function and affecting the noun's form. Understanding these cases is crucial for mastering Russian grammar.
Each word in a sentence will change it's suffix depending on the case it is in. Because there are 3 different genders in Russian and 6 cases, this means that each word can have 18 different forms, that's 32 if you include plural forms!
Not to mention, there's multiple rules for each case depending on a word's ending. For example: собака (dog) is feminine, in the accusative case, it becomes собаку. However, лошадь (horse) is feminine, but in the accusative case, it's still лошадь. These types of rules exist for each case!
Multiply that 32 by at least 2. We're already at 64 different rules to memorize.
MemRussian helps you learn these rules and exceptions with interactive exercises. Download the app to get started!
| Case | Function | Question |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | Subject of the sentence | Who? What? |
| Genitive | Indicates possession | Whose? Of what? |
| Accusative | Direct object of the sentence. Also destination | Whom? What? / To where? |
| Prepositional | Indicates location or subject of discussion | Where? / About whom? About what? |
| Instrumental | Means or instrument of the action | By means of what? |
| Dative | Indirect object of the sentence | To whom? For whom? |
Nominative Case
The nominative case is used for the subject of a sentence. It answers the question "Who?" or "What?" and is the form used to identify the noun in its base state. For example:

Example: Мальчик читает книгу. (The boy is reading a book.) Here, Мальчик (boy) is in the nominative case as it is the subject.
Although nominative is simple, the other cases can be challenging. MemRussian teaches you how to form cases. Download the app now to get started!
Genitive Case
The genitive case indicates possession or the absence of something. It answers the question "Whose?" or "Of what?" For example:

Example: Книга мальчика. (The boy's book.) Here, мальчика (boy's) is in the genitive case as it shows possession.
Learn how to use the genitive case with MemRussian. Download now to enhance your learning!
Accusative Case
The accusative case is used for the direct object of the sentence. It answers the question "Whom?" or "What?" For example:

Example: Я вижу мальчика. (I see the boy.) Here, мальчика (boy) is in the accusative case as it is the object of the action.
MemRussian helps you master the accusative case and more. Download the app for detailed exercises!
Prepositional Case
The prepositional case is used to indicate the location or subject of discussion. It answers the questions "About whom?" or "About what?" and is typically used with prepositions.
Example: Мы говорим о книге. (We are talking about the book.) Here, книге (book) is in the prepositional case as it denotes the topic of discussion.
Master the prepositional case with MemRussian. Download the app to get interactive exercises and improve your understanding!
Instrumental Case
The instrumental case indicates the means or instrument by which an action is performed. It answers the question "By means of what?" For example:

Example: Он пишет ручкой. (He writes with a pen.) Here, ручкой (pen) is in the instrumental case as it denotes the instrument.
Practice using the instrumental case with MemRussian. Get the app now to improve your skills!
Dative Case
The dative case is used for the indirect object of the sentence. It answers the question "To whom?" or "For whom?" For example:

Example: Я дал книгу мальчику. (I gave the book to the boy.) Here, мальчику (boy) is in the dative case as it is the indirect recipient.
Learn how to use the dative case with MemRussian. Download the app today to practice!
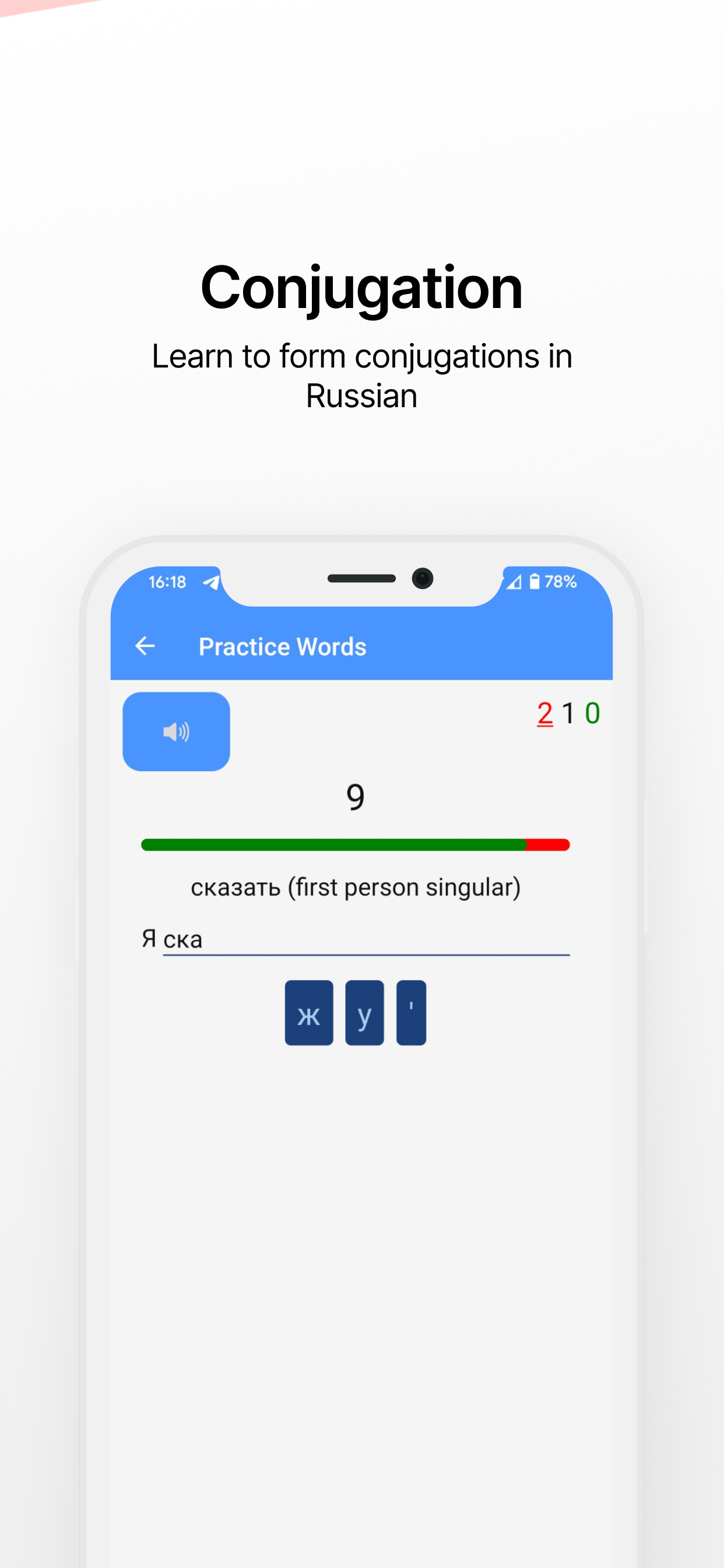
What are verb conjugations?
Verb conjugations involve changing the form of a verb to indicate tense, mood, person, and number. In Russian, verb conjugations are crucial for correctly expressing actions and states of being.
MemRussian teaches you how to conjugate verbs in different tenses and forms. Download the app to get interactive exercises and practice!
Contact
If you have any questions or need support, feel free to reach out to us at contact@memrussian.com.


 Download on IOS
Download on IOS